Why Startups Fail[Part 2 -Early Stage startups]
These chapters of the book discuss the three failure patterns that effect early stage startups: Good idea, bad bedfellows, False starts and False Positives. I also added a summary of a Letter the author wrote to first time founders as it seemed relavent to this stage.
Good idea, bad bedfellows
Quincy hadn't acquired the resources required to capitalize on the promising opportunity.
Founders
Founders lacked industry experience.
Operation complexity was high due to custom fit of clothes. Had to perform a range of activities like design, procurement, pattern making. production quality control and shipping which required close coordination between these activities.
Could not attract Talent due to lack of Industry experience.
Could have used advisors for Network to find experienced managers or could have spent more time acquiring and a stream knowledge.
Spent more time figuring out the challenges of garment Manufacturing to understand their gaps in knowledge.
Team
Team had a lot of specialists which led to a lack of flexibility.
Specialists hired:
- did not have an ownership mentality
- did not appreciate the opportunity
Should have found general managers who worked at startups and who had industry experience
Investors
Tech Investors expected Quincy to perform like a high-tech startup.
Tech VCS had no experience with the apparel industry.
Should have insured that the investors previously had board seats on previous successful apparel startups.
Quincy also has new VCs who could not provide Bridge financing.\
Quincy could have asked two questions
- Will the investor add value in terms of skills and experience?
- Are their risk reward preferences consistent with the startup?
Raising lower than expected money does not leave room for strategic or operational errors
Partners
Due to lack of Industry experience, founders had no relationship with partners.
Quincy's orders were not prioritized due to small size.
It's easy for a mouse to get trampled by an elephant. Threatening lawsuit is not a real option.
Should have done due diligence by checking references from other startups who did business with manufacturer.
Could have given them an equity stake so they would have skin in the game.
good idea, bad bedfellows failure has three patterns:
- complex operations
- inventory of special Goods
- large lumpy Capital requirements
Quincy could have done better by bolstering their resources or constraining their opportunity
If you cannot get the right resources, constrain the opportunity and reduce scope.
Ideas to constrain scope:
- Limit breadth of product line
- Outsource some activities
- focus on a single customer segment
Cons: Outsourcing reduces opportunities to learn and gain industry experience. Additionally, those lessons will be learnt at a later stage when the stakes are higher.
False starts
Triangulate initially started as a generic matching algorithm.
Building without getting into consumers' heads led to a fall start.\
Time is a startup’s most precious resource, and a false start leads to an unnecessary feedback cycle. Each pivot consumes time and cash.
No market is one of the greatest reasons for early startup failure.
Customer value proposition
After all the pivots, Triangulate with wings was building a better mouse trap with no differentiation.
find it hard to compete in a market with strong network effects.\
Marketing- they had to spend too much on marketing to acquire users.
A startup simply does not have enough capital to find marketing required to capture customer attention and establish a new brand.
Profit formula- given marketing spend required and free business model could not generate enough cash initial assumptions were never tested before engineering work.
Bias for action leads to lack of customer development
How to avoid fall start?
To avoid fall starts, startups can use a Double diamond framework to define the problem.
Define and develop a solution must use divergent thinking to generate lots of ideas, followed by convergent thinking picking a good idea for the problem definition phase
Divergent thinking means exploring full range of customer segments and each segment and then full set of needs next to a customer segment and by the end you should have a positioning statement is to find the problem before you choose a specific solution for a lot of alternatives and you were sure you identify the one that best meets your customers needs.
Founders who escape upfront research are likely to complete for your pivots and be more likely to pivot away from bed ideas.
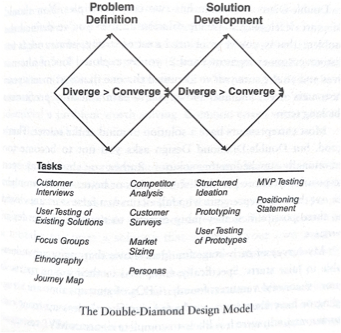
Customer interviews
Ask questions to discover customer problems, some common errors. Assuming you are the customer and you needs are the same is not a good idea.
Pitfalls
Choosing from people who are similar to you.
Not interviewing everyone.
Focusing on early adopters.
Need to distinguish between early adopters and mainstreel customers.
Avoid:
- Ask leading questions
- ask for predictions your solution
- need to focus on discovering and needs.
User testing of existing solutions.
Ask a user about how they currently solve the problem.
Focus groups.
Focus groups can work for products with strong emotional reactions.
Need a trained facilitator to manage a focus group.
Ethnography
Go into the field and observe individuals directly.
Journey map
Plot sequential steps in a customer's buying journey. Search for issues that impact the customers level of satisfaction in each step.
Competitor analysis
Decide which needs to address and which customer targets to segment.\
Plot a row of competitor’s features, and performance. Use columns of the existing solutions.
avoid two traps:
- ignore where your solution fall short
- pretend you don’t have any competitors
Customer survey
Used to validate hypothesis.
Do not ask correspondence to predict future behavior instead ask them how they did something in the past, you can ask great questions until you have an hypothesis to prove:
- Market size estimate
- total addressable market
Do not put your thumb on the scale to impress yourself or investors.
Personas
Create 3 to 5 personas for likely customers.
Brainstorming
Ask people to generate ideas before anyone speaks.
manage meeting to discourage naysayers and critiques.
Prototyping
Create the works like, and looks like prototype.
High Fidelity prototypes can provide a clear road map for engineers to work on the product and give customers a good idea of what the intended solution is.
However, creating high Fidelity prototype takes more time with focus on cosmetic design elements Reviewers might be unwilling to criticize a prototype, and some designers might become attached to a prototype Prototype Testing.
Ask users to choose between two prototypes as they might be reluctant to criticize a single design.
Focus on the solution that delivers value.
MVP Testing.
MVPs are tested differently than need to quickly test assumptions about the demand for your solution. Use stubs for front end or back in functionality.
Constrain either of them to create MVP more quickly.
An error people can meet with MVPs is not to specify a threshold or test success.
Another issue with MVP is revising once assumptions and pivoting too quickly or too slowly. Must ask if the results are false negatives or false positives.
False negative can result from a fidelity MVP or a poorly conducted test.
Positioning Statement
- For [target customer segment]
- dissatisfied with[existing solution]
- due to [unmet need]
- [venture name] offers a [product]
- that provides [key benefits that are differentiated and defensible]
False Positives
False positives are a problem because they give an entrepreneur undue confidence about a particular expansion path.
In Baroo’s case the customer proposition was appealing, but problems were ignored:
- Technology and operations was limited and created difficulties with hiring training, scheduling, motivating and retaining employees.
- Marketing did not have same ipact after unsolicited referrals from property manager suggested building partners would voluntarily steer residence to
- unproven profit formula caused to incur significant losses while they expanding.
Resources
one founders concerns about growth 19
Team
Providers were employees. Which meant they could choose which dogs to care for.
Additionally, they recruited industry specialist
Investors
Fell for the false positive signal and reconsidered preferences about venture growth rate.
Partners
New buildings provided less marketing support than expected and made unreasonable demands.\
They did not carefully vet the buildings and see if there are similar to the initial buildings that they got the positive signal from.
There are two patterns for false positives:
- Solution is tailor made for early adopters and that solution does not meet for a larger mainstream market
- using the demand forecast from early adopters, the start up scales too fast.
Avoid false positives from early adopters by:
- they should conduct early customer researches research that exposes and differences between early adopters and mainstream customers
- When entrepreneurs are surprised by positive responses from earlier adopters they should consider the possibility that the broader market may not respond in the same way.
Use persona to determine what is special about the earlier adopters versus the customers that the startup planned to pursue.
Entrepreneurs, like all people, are psychologically wired to see what they want and hope to happen. Makes it difficult to interpret research results and early performance.
Two more ways entrepreneurs are vulnerable to false positives:
- unexpected success can be seductive.
- the importance of founders understanding their own goals need to understand their preference regarding growth
- self awareness is important.
Letter to a first time founder
Ignore conventional startup advice
Just do it! With research and exploring problem and solution space, startup might have false start or grow too quickly
Be persistent! Cannot recognize false start and be reluctant to pivot.
Bring passion! May lead to overconfidence. Cannot identify false start or false positive.
Grow! Without customer discovery, growth can lead to false start. Create heavy demand on the team if bad bedfellows. Could expose quality problems and depress profit margins.
Focus! Could focus on a small early adopter market.
Be scrappy! Without the right team you’ll end up with bad bedfellows.
Always weigh options and tradeoffs -> do not trust gut instinct[system 1].